Imagine you're thinking of starting a business or maybe you're just curious about the differences between being a 1099 contractor and a W2 employee. Well, look no further! In this article, we'll break down the hourly rate difference between these two employment types, giving you a clear understanding of what to expect and helping you make an informed decision. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let's dive into the intricacies of 1099 and W2 hourly rates.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Definition and Differences
Overview of 1099 and W2
When it comes to employment, it's important to understand the difference between 1099 and W2. These terms refer to the types of employment arrangements and have implications for both employers and employees. The main difference between them lies in the classification of workers and the tax responsibilities associated with each.
A 1099 worker, also known as an independent contractor, is self-employed and is responsible for paying their own taxes. They receive payment on a project basis and do not have an employer-employee relationship with the company they work for. On the other hand, a W2 worker is considered an employee of a company and receives a regular salary or hourly wage. The employer withholds taxes from their paycheck and also provides certain benefits and protections.
Definition of Hourly Rate
Before diving into the specifics of 1099 and W2 employment, let's clarify what an hourly rate is. An hourly rate is the amount of money a worker receives for each hour worked. It is a common method of payment for both 1099 and W2 employees. The hourly rate can vary depending on factors such as experience, industry, and location.
1099 Employment
Independent Contractor Status
As a 1099 worker, you are considered an independent contractor. This means that you work on a contractual basis and are not an employee of the company you work for. You have the freedom to choose when and where to work, and you have control over how you perform your work. However, it's important to note that this freedom comes with certain trade-offs.
Tax Responsibilities
One of the key differences between 1099 and W2 employment is the tax responsibilities. As a 1099 worker, you are responsible for paying both the employer and employee portion of taxes, known as self-employment tax. This includes Social Security and Medicare taxes. It's important to keep detailed records of your income and expenses as you may be eligible for certain tax deductions.
Hourly Rate Calculation
When calculating your hourly rate as a 1099 worker, you need to consider various factors. First, you need to determine your desired annual income. Then, you divide this amount by the number of billable hours you anticipate working in a year. This will give you an estimate of your hourly rate. It's important to consider factors such as business expenses, taxes, and desired profit margin when setting your rate.
Factors Affecting Hourly Rate
Several factors can influence your hourly rate as a 1099 worker. These include industry standards, demand and supply in your field, your level of experience and expertise, and your location. Keep in mind that your rate should be competitive enough to attract clients while still allowing you to cover your expenses and make a profit.
Advantages and Disadvantages
1099 employment offers certain advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, you have more control over your schedule and workload. You also have the potential to earn a higher income since you can negotiate your rates. However, there are also disadvantages. As a 1099 worker, you do not have access to employee benefits such as health insurance or retirement plans. Additionally, you bear the responsibility of finding your own clients and managing your business.
W2 Employment
Employee Status
As a W2 employee, you are considered an employee of the company you work for. You have a contractual agreement with the employer, and they have certain rights and obligations towards you. This includes providing a regular salary or hourly wage, withholding taxes from your paycheck, and offering employee benefits.
Tax Responsibilities
One of the benefits of being a W2 employee is that your tax responsibilities are typically more straightforward compared to 1099 employment. Your employer withholds taxes from your paycheck, including federal and state income taxes, Social Security, and Medicare taxes. This makes it easier for you to stay compliant with tax regulations and ensures that your tax obligations are met.
Hourly Rate Calculation
When determining your hourly rate as a W2 employee, it's important to consider factors such as your desired annual income, the number of hours you will be working, and any additional compensation such as bonuses or overtime pay. Your employer will usually provide you with a pre-determined hourly rate based on these factors.
Factors Affecting Hourly Rate
Similar to 1099 workers, several factors can influence your hourly rate as a W2 employee. Industry standards, demand and supply in your field, your experience level, and geographical location can all affect how much you are paid. Employers often take these factors into account when setting the hourly rate for their employees.
Advantages and Disadvantages
W2 employment comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. As a W2 employee, you are entitled to certain benefits provided by your employer, such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and workers' compensation. You also have a sense of stability and job security. However, you have less control over your schedule and workload compared to 1099 workers. Additionally, you may have slightly less flexibility in negotiating your hourly rate.
Tax Implications
Tax Deductions and Contributions
Both 1099 and W2 employees are eligible for certain tax deductions and contributions. However, the process and rules may vary slightly for each type of employment. As a 1099 worker, you can deduct business expenses such as office supplies, travel expenses, and professional development costs. W2 employees, on the other hand, may be eligible for deductions such as mortgage interest and student loan interest.
Self-Employment Tax
As mentioned earlier, 1099 workers are subject to self-employment tax, which includes the employer and employee portion of Social Security and Medicare taxes. This can be a significant tax burden, as you are responsible for paying both sides of these taxes. W2 employees only pay the employee portion of these taxes, with the employer covering the other half.
Federal and State Taxes
Both 1099 and W2 employees are required to pay federal and state income taxes. The amount of tax owed will depend on your income level, deductions, and other factors. It's important to stay up to date with tax regulations and consult with a tax professional if needed to ensure compliance and optimize your tax situation.
Tax Forms
The tax forms you are required to file will also differ depending on whether you are a 1099 or W2 employee. As a 1099 worker, you will receive a 1099-MISC form from each client you earned income from. You will need to report this income on your annual tax return using Schedule C. W2 employees receive a W2 form from their employer, which summarizes their income and withholding for the year. This information is used to complete their tax return.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Benefits and Protections
Employee Benefits
One of the key advantages of W2 employment is the access to employee benefits. These include health insurance, retirement plans such as 401(k) or pension plans, paid time off, and other perks like employee discounts or wellness programs. These benefits provide financial security and protection, especially in terms of healthcare and retirement planning.
Unemployment Insurance
W2 employees are eligible for unemployment insurance, which provides temporary income replacement in the event of job loss. This serves as a safety net during periods of unemployment and can help cover essential expenses until a new job is secured. 1099 workers, however, are not eligible for unemployment insurance benefits.
Workers' Compensation
In the unfortunate event of a work-related injury or illness, W2 employees are covered by workers' compensation insurance. This insurance provides medical care and wage replacement in case of disability or inability to work. 1099 workers, being self-employed, are responsible for their own worker's compensation coverage, if desired.
Healthcare and Retirement Plans
W2 employees often have the option to participate in employer-sponsored healthcare plans, which can help alleviate the high costs of medical expenses. These plans may include coverage for medical, dental, and vision expenses. Additionally, W2 employees can contribute to retirement plans such as 401(k)s, which provide a means of saving for the future and potentially receiving employer matching contributions.
Cost of Employment
Employer's Perspective
From an employer's perspective, there are additional expenses associated with hiring W2 employees compared to 1099 workers. These expenses include payroll taxes, contributions to employee benefits such as healthcare or retirement plans, and compliance with labor laws and regulations. Employers must carefully consider these costs when making hiring decisions.
Additional Expenses for W2 Employee
As a W2 employee, you may also incur additional expenses compared to being a 1099 worker. These can include commuting costs, professional development expenses not covered by the employer, and potentially higher taxes due to the employer withholding taxes from your paycheck. It's important to budget for these additional expenses when considering a W2 position.
Profit Margin Considerations
When setting your rates as a 1099 worker, it's crucial to consider your profit margin. Because you are responsible for paying your own taxes and covering business expenses, you need to ensure that your rates allow for a reasonable profit after all expenses are accounted for. This profit serves as your sole income and should be sufficient to cover your personal expenses and savings goals.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Industry Factors
Industry Standards
Different industries have different standards when it comes to hourly rates and employment arrangements. It's important to research and understand the norms within your specific industry. Factors such as skill level, experience, and demand for your services can all influence the prevailing hourly rates.
Demand and Supply
The level of demand and supply within your industry can impact your hourly rate as well. If there is high demand for your skills and few qualified professionals available, you may be able to command a higher rate. Conversely, if there is an oversupply of workers in your field, you may need to adjust your rates to remain competitive.
Experience and Expertise
Your level of experience and expertise also plays a role in determining your hourly rate. Clients and employers may be willing to pay more for individuals with specialized knowledge and a proven track record of success. It's important to leverage your skills and experience when negotiating your rates, regardless of whether you are a 1099 or W2 employee.
Location
Geographical location can have a significant impact on hourly rates due to variations in cost of living and local economic factors. Hourly rates in large metropolitan areas may be higher compared to rural or less economically developed regions. Consider the local job market and economic conditions when evaluating hourly rate expectations.
Negotiation and Market Factors
Evaluating Compensation Offers
Whether you are a 1099 or W2 employee, it's essential to carefully evaluate compensation offers to ensure they are fair and aligned with your expectations and the market standards. Consider factors such as the hourly rate, benefits package, potential for career growth, and overall job satisfaction. Don't be afraid to negotiate and clarify any discrepancies or concerns.
Market Research
Before entering into any employment arrangement, it's crucial to conduct market research to understand the prevailing hourly rates in your industry and location. This information will help you set realistic expectations and negotiate effectively. Research online job boards, industry forums, and professional networks to gather insights from others in your field.
Negotiating Rates
As a 1099 worker, negotiating your rates is a common practice. It's important to approach rate negotiations professionally and confidently. Consider factors such as your experience level, the scope of work, the client's budget, and the market rate. Present a persuasive argument for why your proposed rate is fair and aligns with the value you bring to the project or role.
Competitiveness
Whether you choose to be a 1099 or W2 employee, it's vital to remain competitive in the job market. Stay up to date with industry trends, continuously enhance your skills, and network with professionals in your field. By continuously improving and positioning yourself as an expert, you increase your chances of securing opportunities and negotiating higher rates.
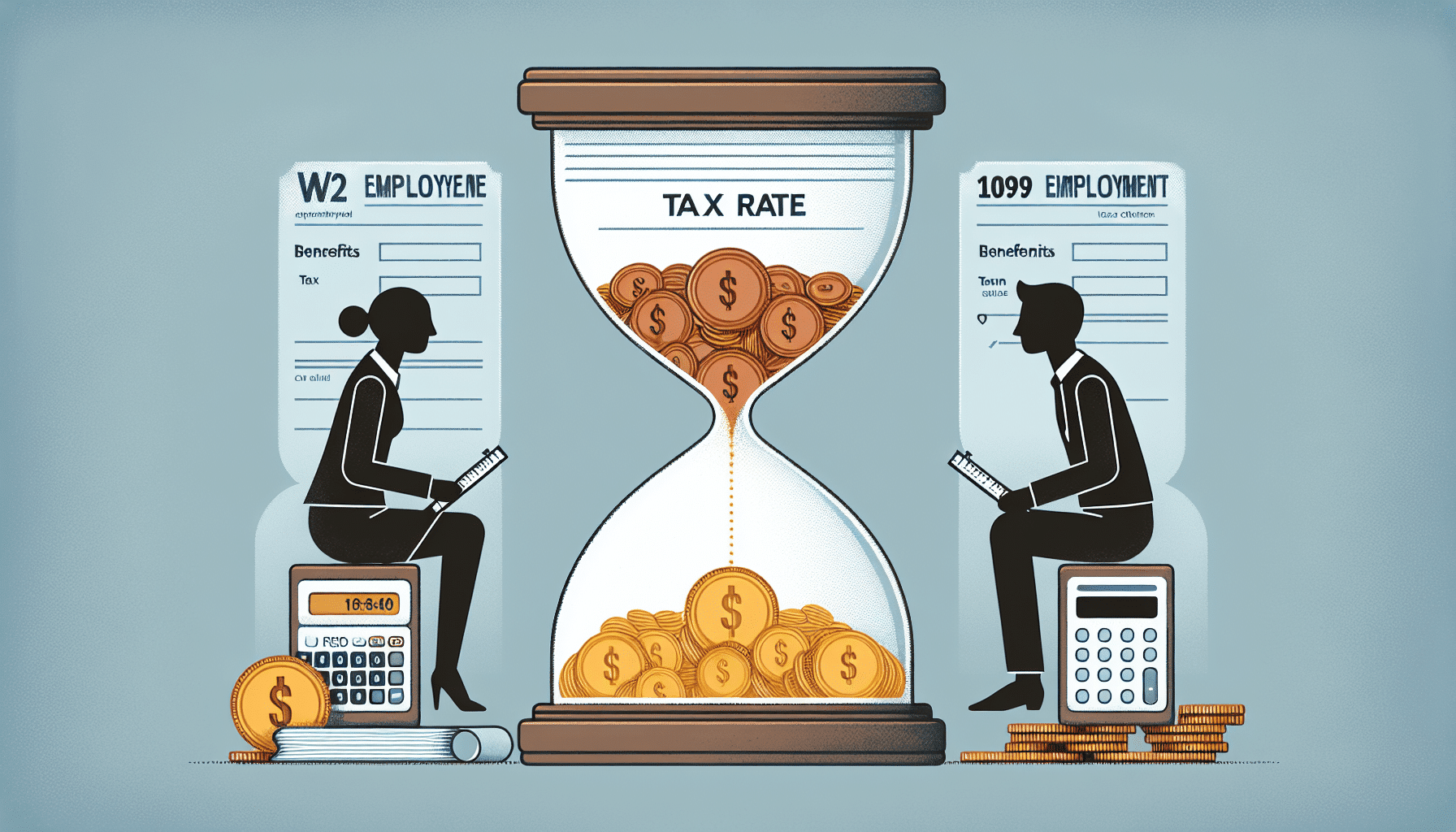
Transition from 1099 to W2
Motivations for Transition
At some point in your career as a 1099 worker, you may consider transitioning to W2 employment. There can be various motivations for this decision. Some individuals seek the stability and benefits that come with being a W2 employee. Others may desire a better work-life balance or a change in their career trajectory. It's important to clearly identify your motivations when considering this transition.
Process and Considerations
Transitioning from 1099 employment to W2 employment involves several considerations and steps. You will need to identify suitable job opportunities, update your resume and cover letter to highlight your relevant skills and experience, and prepare for interviews. It's important to approach the transition process strategically and plan accordingly to ensure a smooth and successful shift.
Financial Impact
Moving from 1099 to W2 employment may have financial implications. As a W2 employee, you may receive a steady and reliable income but may have a lower hourly rate compared to working as an independent contractor. Ensure that you evaluate the financial impact of this transition and consider factors such as employee benefits and taxes to make an informed decision.
Legal and Contractual Obligations
When transitioning from 1099 to W2 employment, it's important to be aware of any legal or contractual obligations you may have as an independent contractor. Review your contracts and agreements carefully to understand any restrictions or notice periods that may be in place. It's also important to maintain open and honest communication with your clients throughout the transition process.
Conclusion
Understanding the hourly rate difference between 1099 and W2 employment is crucial when navigating the job market. Each employment arrangement has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it's important to choose the option that aligns best with your goals and priorities. Consider factors such as tax responsibilities, benefits, career growth opportunities, and financial stability when making your decision. Remember to research the market, negotiate effectively, and stay informed about industry standards. By doing so, you can make informed choices and pave the way for a successful career.